- Uncategorized
- Blog
- Getting Started
- Models
- How Do I?
- Mobile SDK
- Android API
- Mobile SDK Overview (Android)
- App Development
- Creating Your SCiO App
- Get SCiO Version
- Read SCiO Battery Status
- Check if calibration is needed
- Prerequisites
- App Registration
- Create Application (Android Studio)
- Import API
- Set Permissions for BLE API
- Rename SCiO
- Login
- Discover SCiO Sensor
- Connect to SCiO Sensor
- Scan a Sample
- Calibrate SCiO Sensor
- SCiO Device callback
- Get the Model ID
- Get CP Models
- Send the Scan to the Cloud for analysis
- Getting Model Results
- iOS API
- Android API
- What Is?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I have more than one SCiO Sensor synced to my phone?
- What researcher development tools are available with my SCiO?
- SCiO Hardware Components
- SCiO Software Components
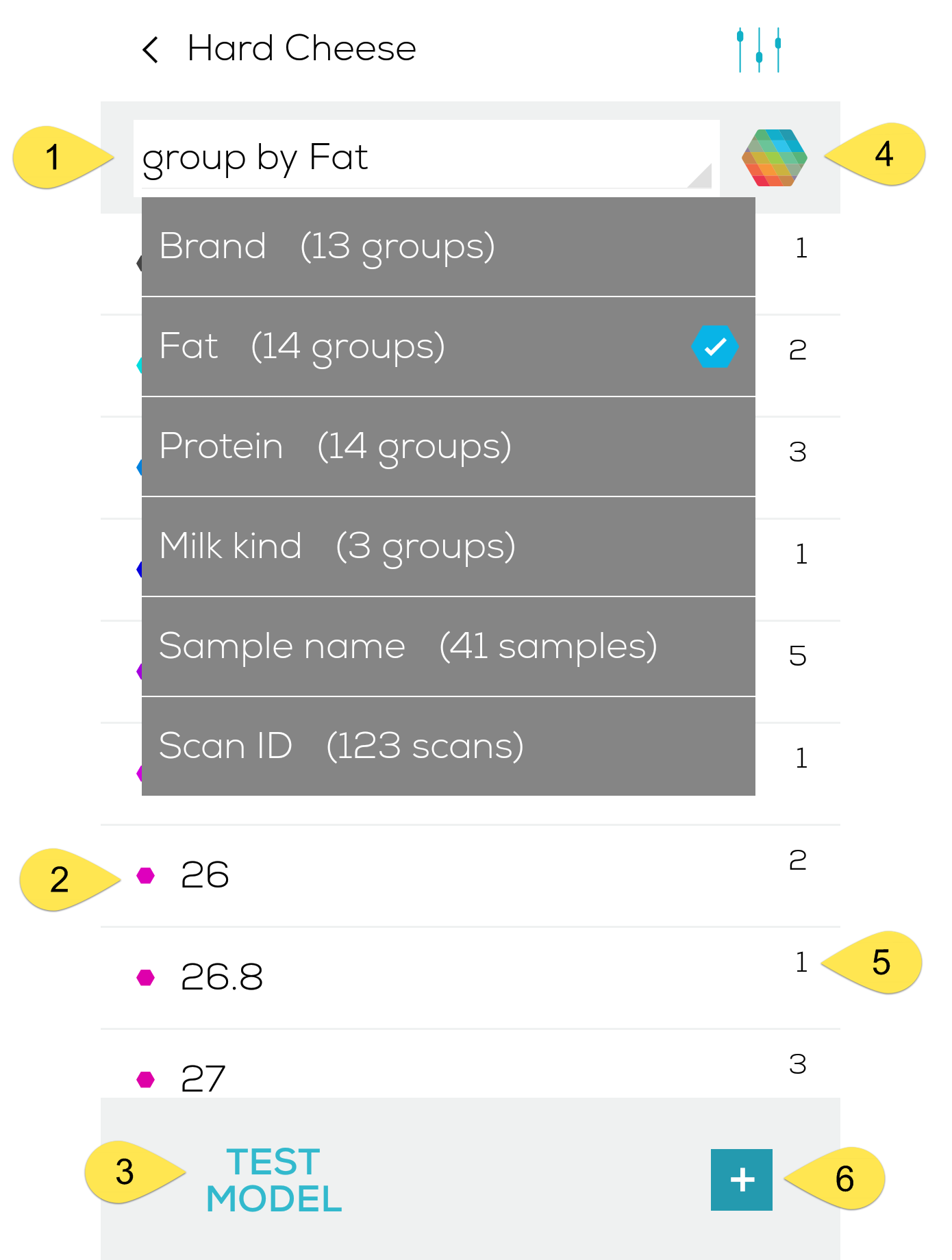
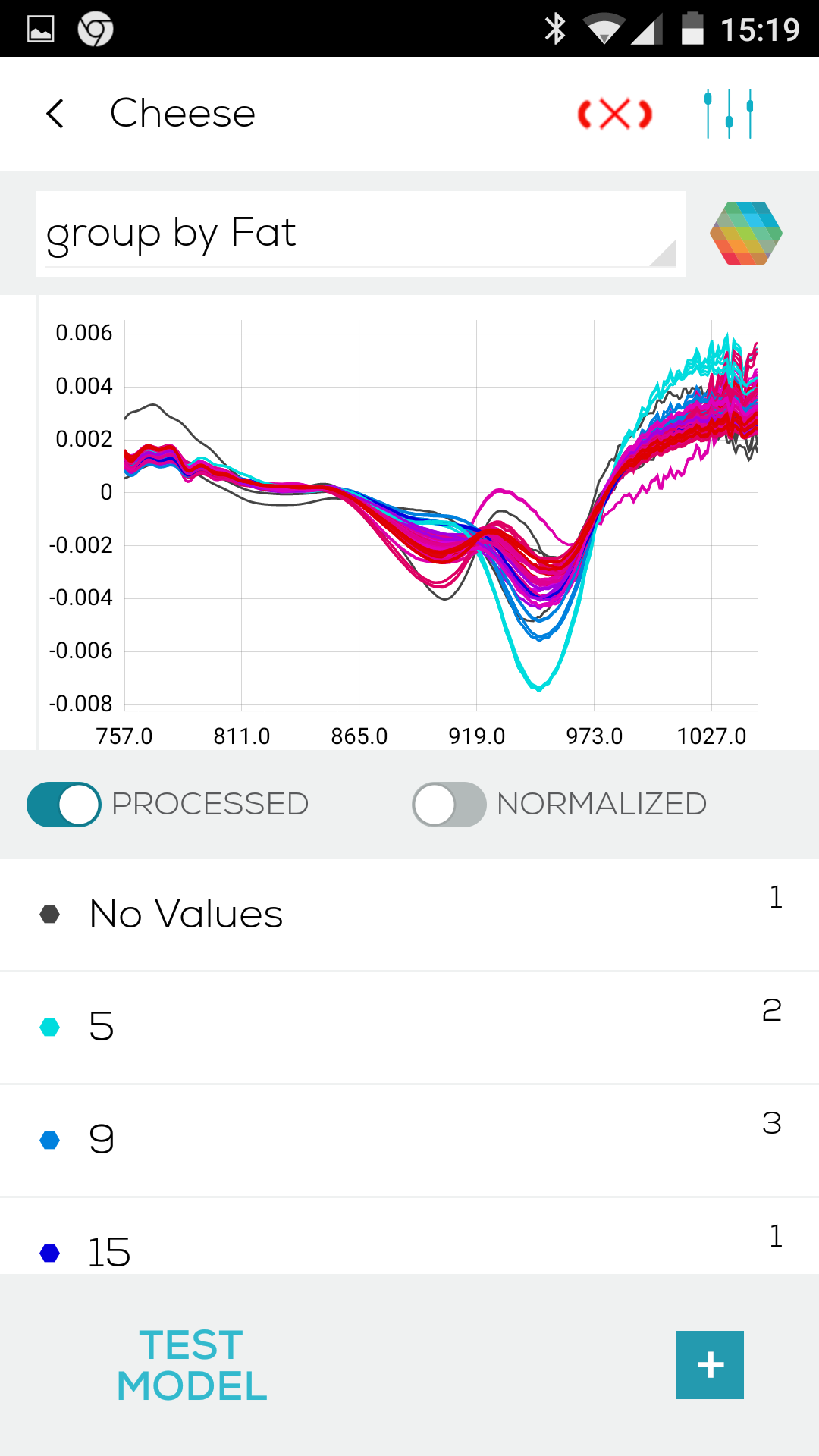
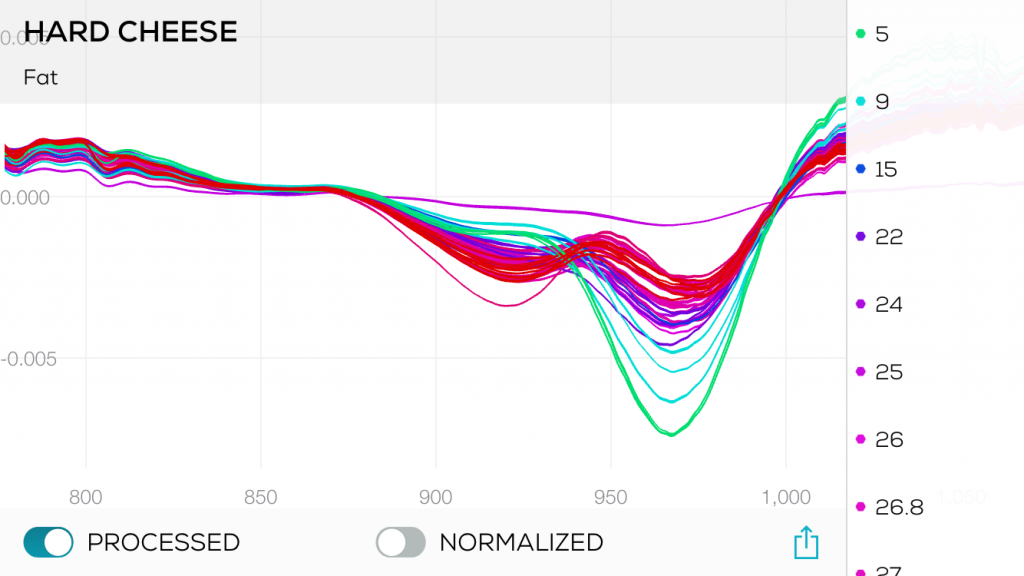
- What is the minimal amount of samples I need to scan to create a working chemometric model?
- What are the key points for a good data collection?
- Can you help me with the analysis?
- Will you provide me tools to build and test models?
- I want to analyze my data with my own tools, can I do that?
- Can SCiO work with an external light source?
- Can SCiO work outdoors?
- How often does SCiO need to be calibrated and why?
- What is the Solid Sample Holder used for?
- How should I hold SCiO when scanning samples?
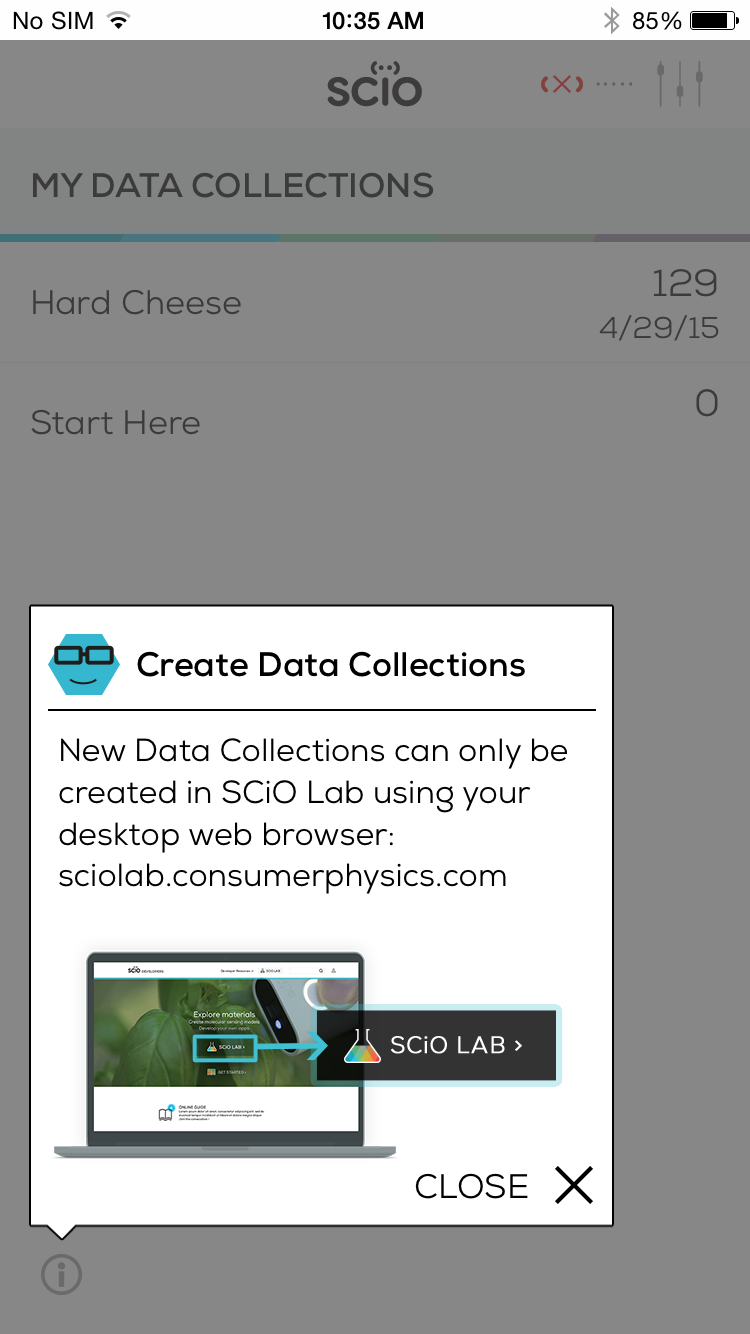
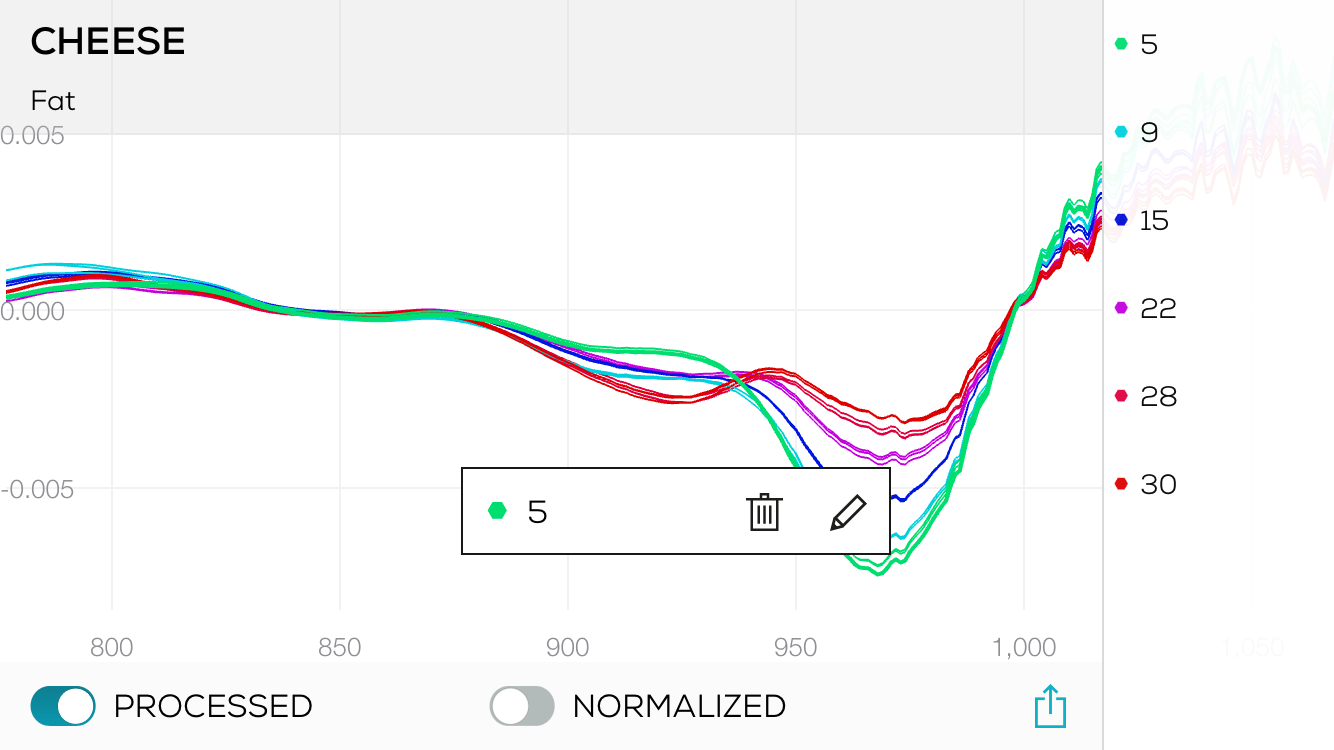
To start work on a new Data Collection, you’ll need to log into SCiO Lab from a web browser at: sciolab.consumerphysics.com.
Data Collections can only be created in SCiO Lab.